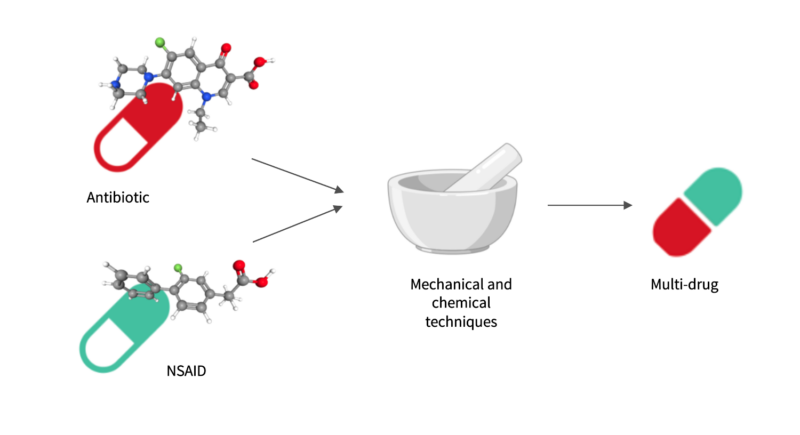
Most drugs on the market have properties that could be improved, of which solubility is the most common. Solubility is important because it affects absorption, that is, the amount of drug that enters the body. Low absorption means that the drug cannot reach its destination and does not have sufficient effect. If this happens, the dose must be increased, so raising not only the costs of the treatment but also the side effects. Various different techniques can be applied to solve this problem, one of which involves binding the drugs to other molecules that improve the solubility of the drug without affecting its action. Sometimes, these molecules can be other drugs, so that in addition to improving the properties, we can create a “multi-drug” that is very useful in combination therapies.
The aim of the study is to combine two drugs: an antibiotic and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), such as flurbiprofen. To this end, we carried out mechanochemical syntheses, such as grinding, which enable the formation of bonds between the two drugs, giving rise to salts. Once we had obtained the drug-drug salts, we then conducted characterization, stability and solubility studies on them to assess their viability.
Keywords: antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, solubility, absorption, multidrug.
Directed by: Alicia Domínguez Martín