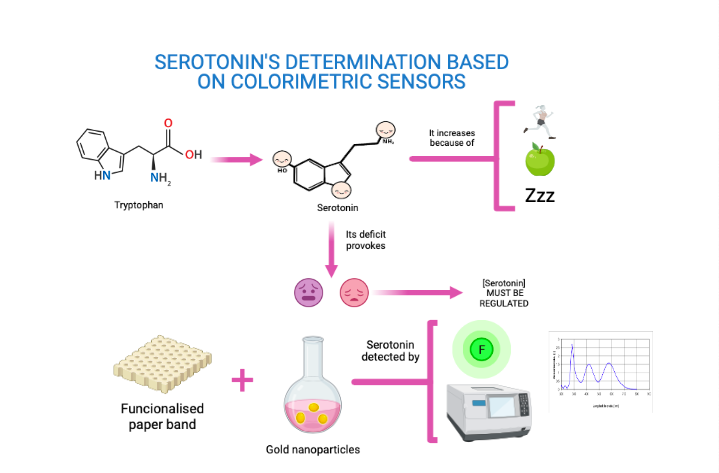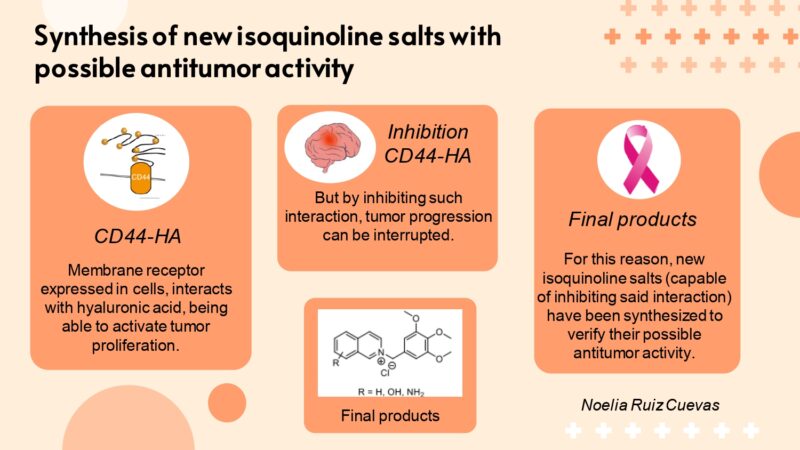
CD44 is a membrane receptor found in various types of cells in our body. This receptor binds mainly to hyaluronic acid (HA). The interaction of HA with CD44 induces changes that trigger rapid growth (proliferation) of cancer cells. Inhibition of this interaction could therefore interrupt tumour progression.
There is a specific place (small pocket) in the structure of CD44 in which small molecules could be introduced that would act as inhibitors of tumour activity. The first structures to show inhibitory activity when interacting with this pocket were molecules known as tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives. However, it is difficult to assess the capacity of these molecules as possible antitumor agents due to their poor solubility. The main objective of this research is therefore to synthesize a series of isoquinoline salts that have good solubility in water, so facilitating the biological evaluation of these molecules.
These molecules are obtained via the reaction of isoquinoline with a chemical compound, the 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl group, and the introduction of different substituents in its structure, specifically in a structure known as an aromatic ring. These substitutions enable us to study the structure-activity relationship and the effect on the binding of the molecules to the aforementioned pocket in CD44.
Keywords: cancer; inhibitors; hyaluronic acid; CD44; isoquinoline.
Directed by: Olga Cruz López