Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease. This disease is based on an accumulation of triglycerides in the liver (steatosis), which can progress to chronic liver inflammation, fibrosis and cirrhosis. It is also associated with an increased risk of developing liver cancer. NAFLD is related to many metabolic factors such as obesity or type 2 diabetes mellitus.
In addition, the aforementioned diseases are related to an imbalance in the composition of the intestinal microbiota (dysbiosis). We can therefore assume that the restoration of the composition of the intestinal microbiota could contribute to the treatment of this disease.
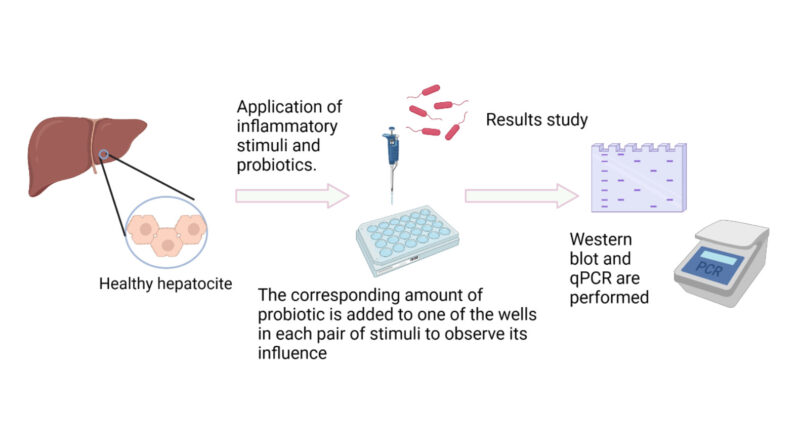
The objective of the study is to assess the effects of the supernatant of the probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei, which is the medium in which these bacteria have grown and left products of their metabolism, on a hepatic cell model in a proinflammatory environment. A positive effect (e.g. anti-inflammatory) of this probiotic would contribute to improving treatment expectations, not only for early stages of this disease but also for possible anti-cancer or protective treatments.
Keywords: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, probiotics, liver, liver disease, in vitro model
Directed by: Ana I. Álvarez Mercado
Leave a Reply