Cancer is a disease that begins when a cancerous cell manages to evade the main regulatory mechanisms of the cell cycle and begins to proliferate uncontrollably. It is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, so the search for new therapies is essential.
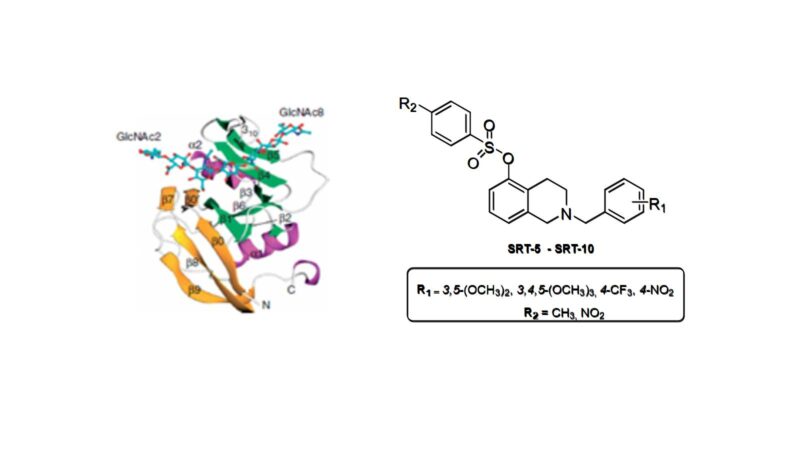
CD44 is a glycoprotein whose increased expression makes tumors more resistant to cancer treatments. Its ligand is hyaluronic acid (HA) and after binding, signaling cascades are activated that contribute to increased cell proliferation, migration and tissue invasion.
Tetrahydroisoquinoline (THIQ) inhibits binding between CD44 and HA. With this in mind, in this Master’s Thesis, we propose the synthesis of 10 isoquinolin-5-ol derivatives. We will then assess the capacity of these derivatives to act as antitumor agents by inhibiting binding between CD44 and HA.
Keywords: Cancer; CD44; Hyaluronic Acid; Tetrahydroisoquinoline; Inhibitors.
Directed by: María Dora Carrión Peregrina
Leave a Reply