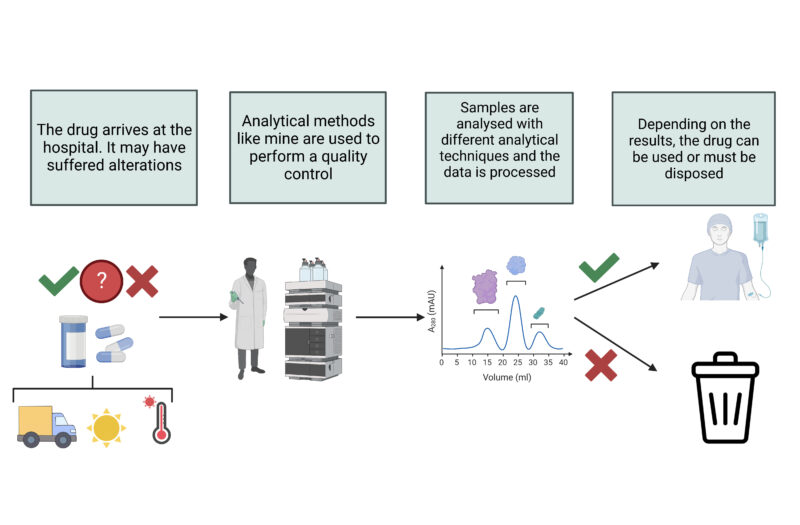
When we get ill or suffer from a disease, we go to the doctor in search of a treatment that will make us better. With rare diseases, biotechnological drugs are used as treatments because they are more effective than their chemical counterparts. Biotechnological drugs are based on therapeutic proteins that are specifically designed to treat a particular illness. However, they tend to be more fragile and unstable than chemical ones. They can suffer alterations during the production phase and during shipping.
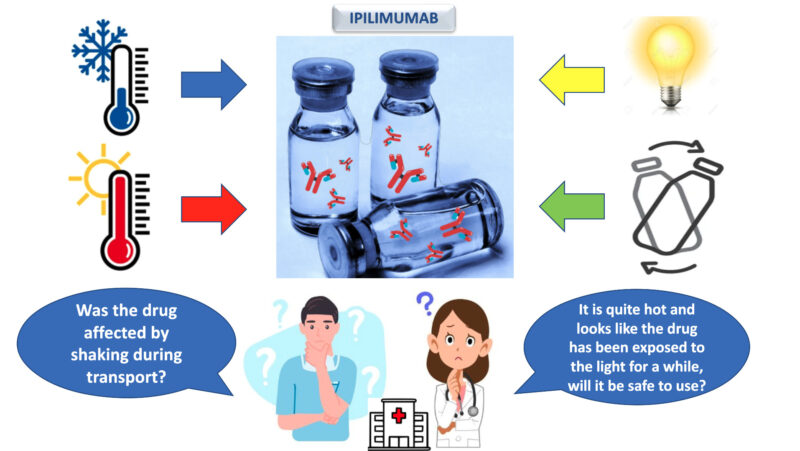
They are more sensitive to environmental conditions such as exposure to the sun, temperature changes and brusque movements (for example during transport). Conscientious quality control is therefore essential before administration to the patient.
My Master’s project focuses on the quality control of Ipilimumab, a therapeutic protein used in hospitals for treating melanomas and colorectal cancers among others. The method I apply involves subjecting the drug to controlled stress conditions, such as extreme temperatures, freezing, stirring, etc. I then compare the data obtained from the stress tests with the data for an unstressed control sample. The data are obtained using analytical techniques such as Liquid Chromatography.
In this way, recommendations can be made regarding the correct handling of this drug, and we can avoid using it if it shows signs of degradation.
Keywords: Therapeutic proteins- Environmental conditions- Quality control- Analytical techniques
Directed by: Natalia África Navas Iglesias