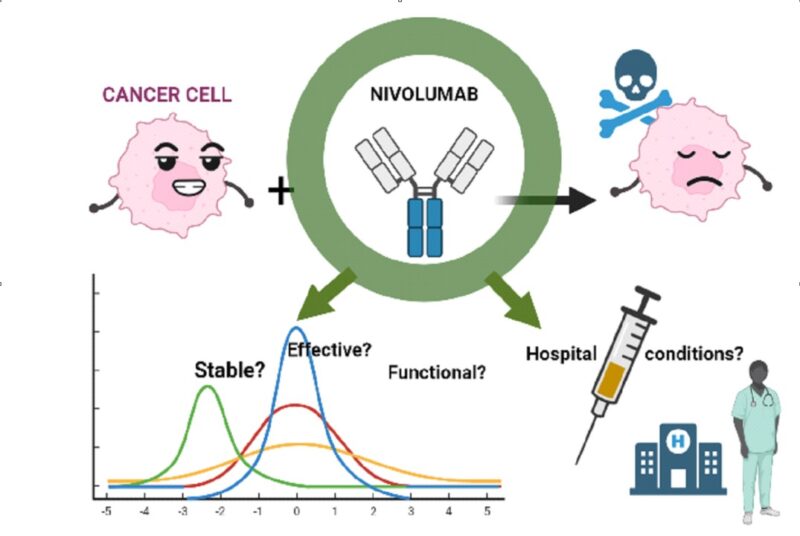
Cancer, which involves an uncontrolled increase in cell proliferation and growth, remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Our immune system tries to eliminate this excess proliferation of cells from the body. However, cancer has mechanisms that help it evade the actions of the immune system, making it very difficult to fight effectively.
New therapies and drugs are being developed to combat this disease. One such drug is nivolumab, which is used to treat lung cancer, among others. However, it has an important disadvantage in terms of its high price and its loss of efficacy in certain storage conditions or during hospital use, because of its protein nature. In this project a quantitative technique (MicroScale thermophoresis) is used to analyze the efficacy and stability of nivolumab over time and when subjected to conditions similar to those applicable during handling of the drug in hospitals.
Keywords: cancer; nivolumab; efficacy; stability; MicroScale thermophoresis
Directed by: Jesús Hermosilla Fernández