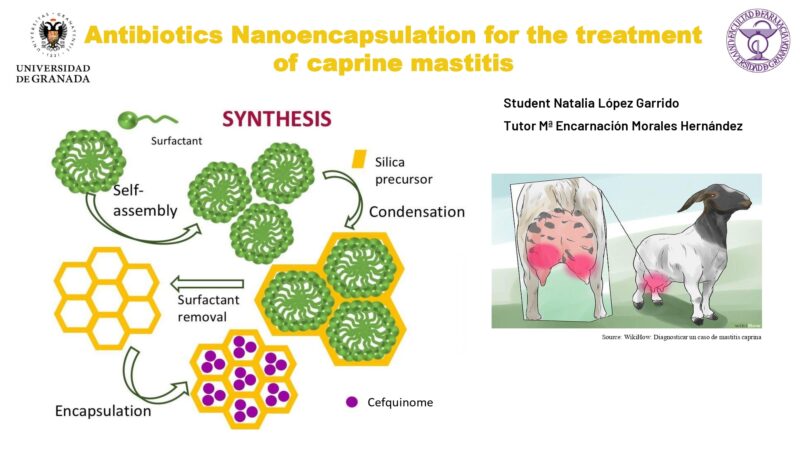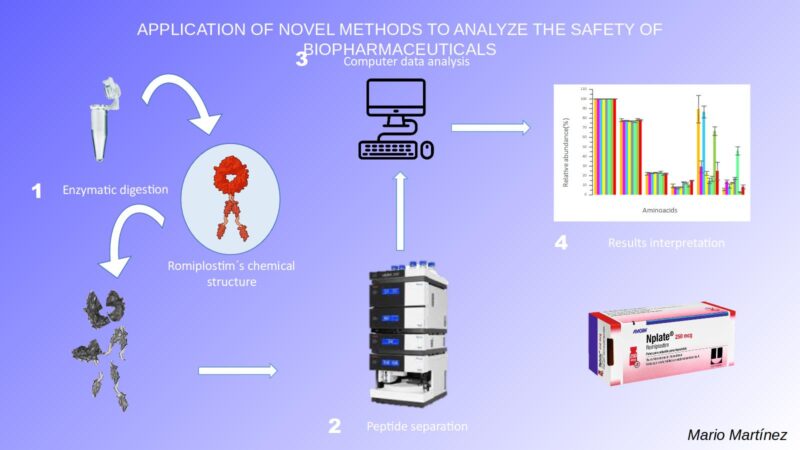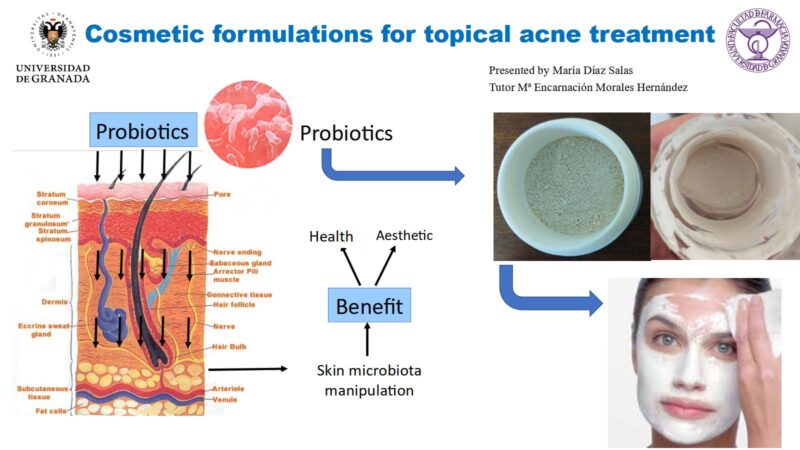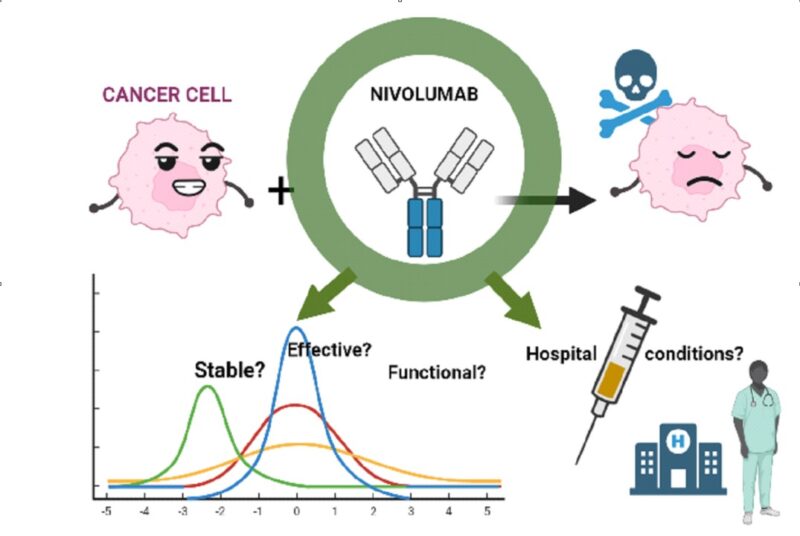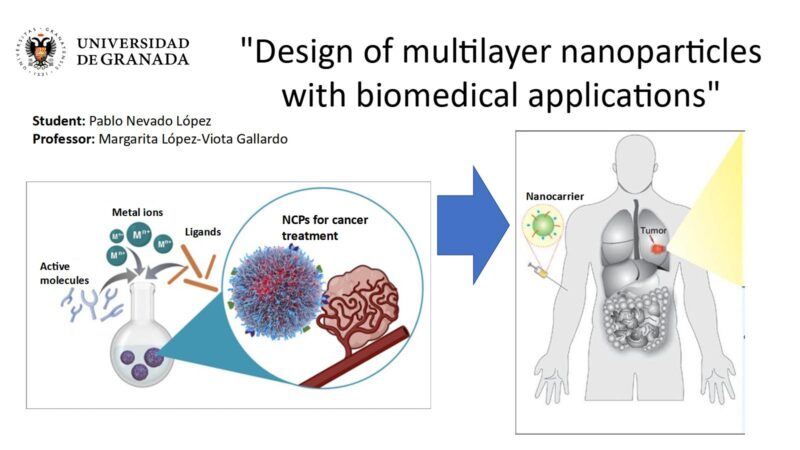
Various different therapeutic strategies are applied against cancer, such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy and the different combinations between them. Pharmaceutical nanotechnology is a science that has long been applied in the preparation of drug delivery vehicles. Many interesting innovations and therapeutic applications have emerged in recent years. The purpose of these systems is to protect the drug (or active ingredient), modify some of its characteristics and improve its distribution in body cells, among others.
In this study, we propose to design a new drug transport system on a nanometric scale. To this end, nanoparticles made up of two layers of polymers (chemical compounds) were designed. This multilayer is made of PLGA (poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) and coated with chitosan. The nanoparticles contain an active ingredient called 5-Fluorouracil, which is classified as a cytostatic and is used to treat cancer.
Keywords: Pharmaceutical nanotechnology; cancer; drug delivery system, polymers, 5-Fluorouracil.
Work directed by: Margarita López-Viota Gallardo