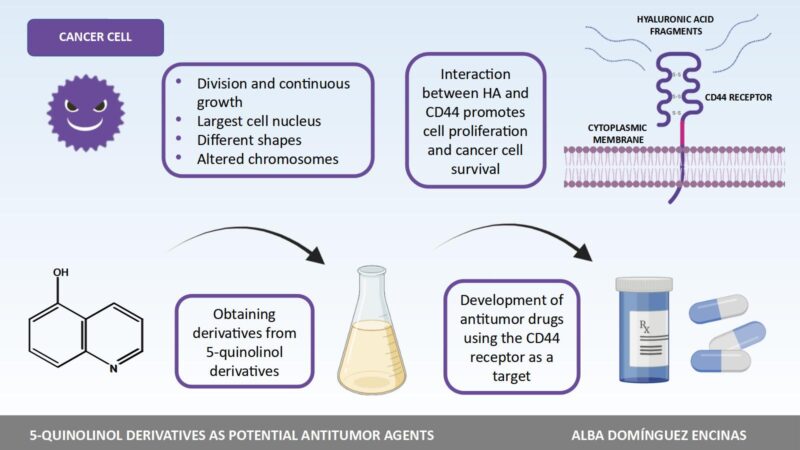
Nowadays, cancer is the second greatest cause of death worldwide, with an estimated 10 million deaths in 2020. Although many chemotherapy drugs are used in clinical practice, we still face two challenges: (a) some patients acquire resistance to anti-tumour drugs after long periods of treatment; (b) these drugs can have toxic effects on healthy cells and tissues. The development of new anti-cancer drugs is therefore essential.
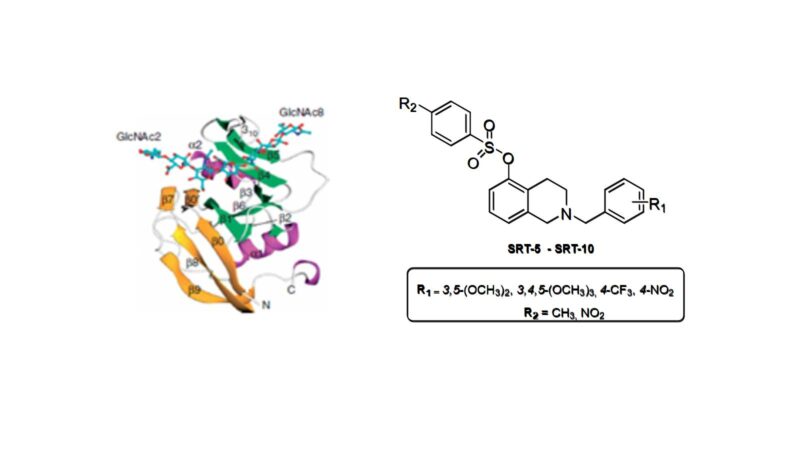
Research shows that hyaluronic acid (HA) can encourage the growth and development of tumours as it interacts with the CD44 protein located on the surface of tumour cells. It has also been noted that compounds known as isoquinoline derivatives can inhibit tumour cell growth (antiproliferative activity) by inhibiting HA-CD44 binding.
In this master’s thesis we aim to synthesize a series of 5-quinolinol derivatives (isoquinoline derivatives) to evaluate their antiproliferative activity and the process by which they inhibit HA-CD44 binding.
Keywords: cancer; CD44; hyaluronic acid; quinolinoline; inhibitors
Directed by: Mª Dora Carrión Peregrina
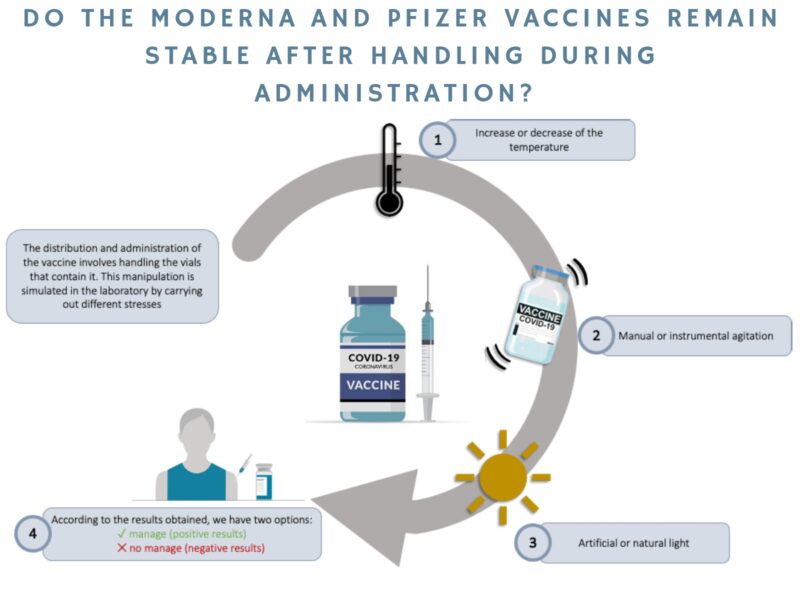
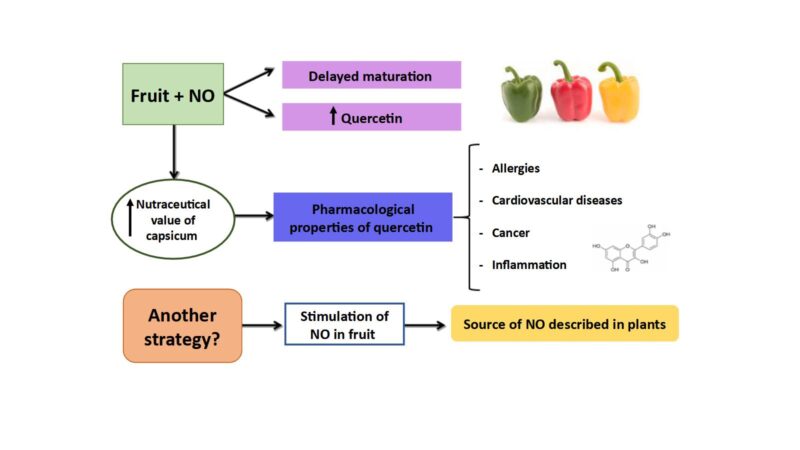 This research was carried out in the Antioxidants, Free Radicals and Nitric Oxide in Biotechnology and Agri-Food Research Group (Zaidín Experimental Station, CSIC, Granada). In recent years, this group has been investigating the possible contribution that peppers can make to a better state of health, thanks to the fact that they contain compounds of pharmacological and therapeutic interest. In collaboration with the University of Malaga and the MEDINA Foundation, we conducted metabolomic and transcriptomic studies to analyse a series of metabolic pathways that lead to the synthesis of molecules with this potential capacity. These molecules are also modulated by nitric oxide (NO), a molecule whose functions in the physiology of both animal and plant cells are increasingly recognised. This Master’s Thesis takes a step further in this strategy which, together with other metabolomic data recently obtained, has allowed the group to focus its research on quercetin, one of the flavonoid compounds present in peppers, which has a number of pharmacological properties.
This research was carried out in the Antioxidants, Free Radicals and Nitric Oxide in Biotechnology and Agri-Food Research Group (Zaidín Experimental Station, CSIC, Granada). In recent years, this group has been investigating the possible contribution that peppers can make to a better state of health, thanks to the fact that they contain compounds of pharmacological and therapeutic interest. In collaboration with the University of Malaga and the MEDINA Foundation, we conducted metabolomic and transcriptomic studies to analyse a series of metabolic pathways that lead to the synthesis of molecules with this potential capacity. These molecules are also modulated by nitric oxide (NO), a molecule whose functions in the physiology of both animal and plant cells are increasingly recognised. This Master’s Thesis takes a step further in this strategy which, together with other metabolomic data recently obtained, has allowed the group to focus its research on quercetin, one of the flavonoid compounds present in peppers, which has a number of pharmacological properties.